Is Super Glue Safe?
Exploring Ethyl Cyanoacrylate’s Key Properties
Super glue fixes everything in seconds, but its safety is often questioned. What exactly makes this instant adhesive unique?
Ethyl cyanoacrylate, the main component in super glue, forms strong bonds quickly but has specific safety limitations. It’s non-conductive when cured, not food-safe, and has low toxicity with precautions needed during use.

For those using super glue in specialized applications, understanding these three aspects is crucial. Let’s break down each concern with practical details.
Is Ethyl Cyanoacrylate Conductive? A Clear Answer for Electronics Use
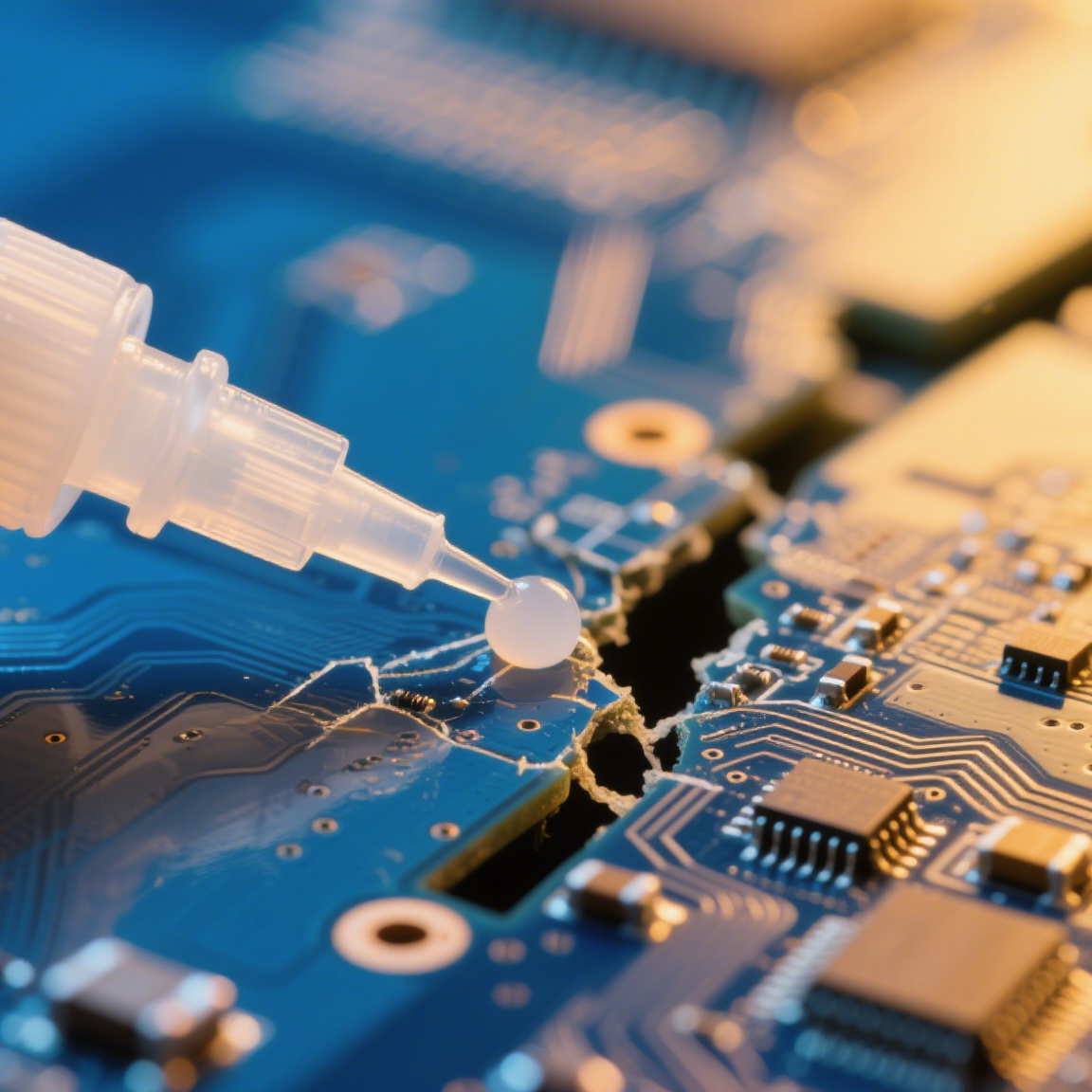
When your circuit board needs quick fixing, can you trust super glue not to interfere?
Cured ethyl cyanoacrylate is non-conductive, making it suitable for basic electronics repairs. The polymer structure blocks electrical currents, preventing short circuits in bonded components.
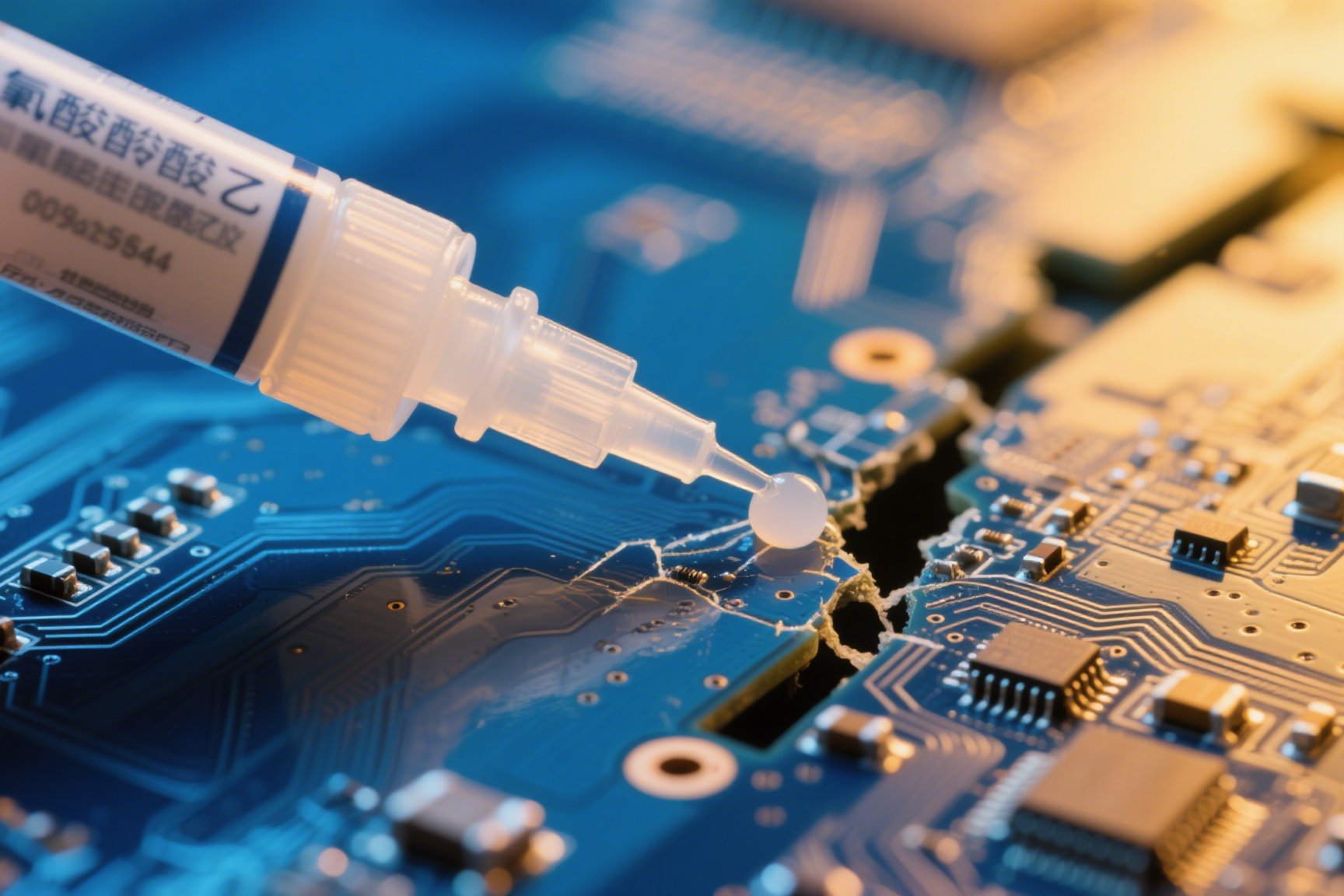
The insulating properties vary slightly depending on application conditions:
| Scenario | Conductivity Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Pure cured adhesive | Non-conductive | Safe for low-voltage circuits |
| Contained metal dust | Possible conduction | Clean surface before application |
| High humidity environment | Minimal effect | Allow full curing time |
Working with circuit boards myself, I’ve found these practical points help:
- Always apply thin layers – thick glue takes longer to fully cure
- Remove excess adhesive before hardening
- For high-voltage applications, consider specialized electronic adhesives
Is Ethyl Cyanoacrylate Food Safe? The Hard Truth About Kitchen Repairs
That broken teacup seems like an easy super glue fix, but should you drink from it afterwards?
Standard ethyl cyanoacrylate adhesives are not food-safe. They lack FDA approval for direct food contact and may release harmful substances when exposed to heat or liquids.
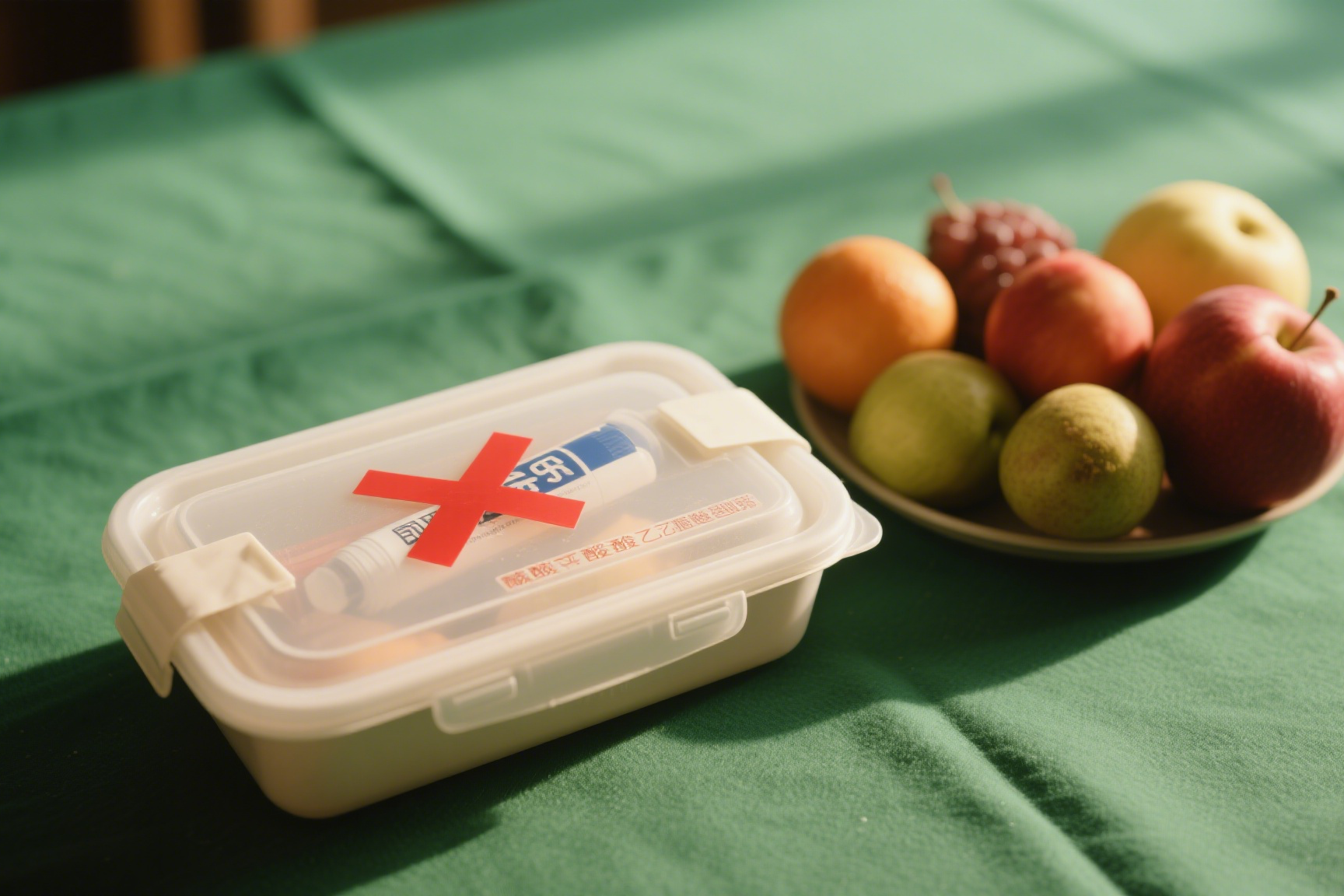

Several factors make super glue unsuitable for food-related repairs:
-
Chemical Leaching
- Uncured residues can dissolve in hot liquids
- Acidic foods may degrade the bond over time
-
Temperature Sensitivity
- Becomes unstable above 120°F (49°C)
- Dishwasher use accelerates breakdown
-
Physical Hazards
- Brittle nature may create sharp edges
- Small fragments could chip off into food
For kitchen items needing repair, I recommend these alternatives:
- Food-grade epoxy resins (look for NSF certification)
- Ceramic adhesives specifically labeled for dishware
- Heat-resistant silicone for non-load-bearing joints
Is Ethyl Cyanoacrylate Non-Toxic? Understanding the Safety Balance
The warning labels seem scary – how dangerous is super glue really?
Cured ethyl cyanoacrylate has low toxicity, but liquid form requires careful handling. Skin bonding and fumes present the most common hazards during application.

Toxicity comparison between forms:
| Form | Primary Risk | Exposure Duration | First Aid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid | Skin bonding/eye damage | Immediate | Acetone removal (skin), water flush (eyes) |
| Curing | Fume inhalation | 30-60 seconds | Ventilation, leave area |
| Cured | Ingestion hazard | Persistent | Medical consultation if swallowed |
Through personal experience, I’ve learned:
- Always work in ventilated spaces
- Wear nitrile gloves to prevent skin bonds
- Keep pets away during application
- Store upright in child-proof containers
For medical applications, only formulated cyanoacrylates (like 2-octyl cyanoacrylate) should be used under professional guidance.
Conclusion
Super glue’s ethyl cyanoacrylate offers strong, quick bonds but requires specific safety knowledge. Remember it’s non-conductive for electronics, not food-safe, and needs careful handling despite low toxicity.